
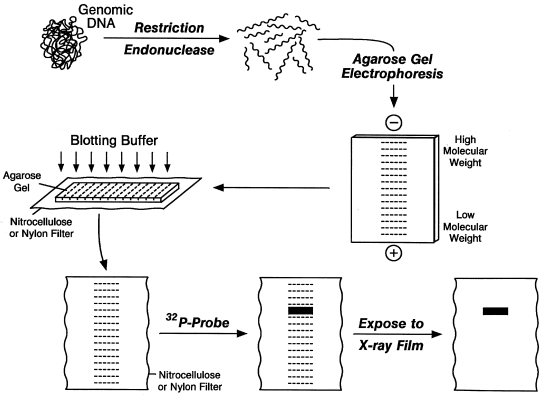
Thus, molecular genetic studies of FMR1 are utilized to confirm a clinical diagnosis of fragile X syndrome, and perhaps just as importantly, to exclude an alteration in FMR1 as an explanation for nonspecific mental retardation in a patient. The variable phenotype occurs related to variation in FMR1 expression mediated by the extent of CGG repeat expansion and a secondary epigenetic feature: the aberrant hypermethylation of CpG dinucleotides contained in the CGG repeat segment and surrounding regions of the gene (9). Insta bility of a CGG repeat segment contained within FMR1 exon 1 is the molecular basis for nearly all mutations (>99%) in the gene and leads to reduced or complete loss of FMRP (3–8). Patients with the syndrome often vary dramatically in presentation with a range of intellectual and behavioral deficits, and provide a diagnostic challenge for clinicians due to the subtle nature of the physical phenotype (1,2). lessįragile X syndrome, caused by the loss or diminution of the FMR1 (FRAXA - chromosomal locus Xq27.3) encoded protein, FMRP, results in mild to moderate mental retardation as its hallmark. Each lane contains approx 2 µg of digested DNA. 2.DNA profiles in eight domestic pigs (1–8) and two wild boars (9 and 10) using digoxigenin labeling and color detection of a porcine minisatellite isolated from a genomic pig library, a to d indicate the alleles detected at this locus. The blots had been hybridized before to at least two other probes. 1.5- to 2 µg DNA digests were loaded per individual. F, father M, mother Dl and D2, their daughters Ul, unrelated female U2, unrelated male 1 to 6, six related individuals from a captive population. 1.Examples of DNA fingerprints in three different species using digoxigenin-labeled RNA minisatellite 33.15 and color detection: ( a) in man, ( b) in the common marmoset ( Callithrix jacchus), and ( c) in the Waldrapp ibis ( Geronticus eremita). 1 and 2, respectively) and also for blots that have been screened several times with both radioactively labeled or digoxigenin-labeled probes (1).Fig. The method can be applied to both multi- and single-locus probes ( seeFigs. The following procedure describes the hybridization of digoxigenin-labeled RNA minisatellite probes ( seechapter 12 ) to Southern blots of different species and visualization of the DNA banding patterns by color detection. In addition, a nonradioactive Southern blot hybridization protocol for the analysis of mtDNA large deletions is also described.
This method allows the detection of low percentage of mutant heteroplasmy. In this chapter, we describe a multiplex PCR/allele-specific oligonucleotide (ASO) hybridization method for the screening of 13 common point mutations. Additionally, Kearns–Sayre syndrome and Pearson syndrome are caused by large mtDNA deletions. Clinical heterogeneity may be due to the degree of mutant load (heteroplasmy) and distribution of heteroplasmic mutations in affected tissues. Most of the pathogenic mtDNA point mutations are present in the heteroplasmic state, meaning that the wild-type and mutant-containing mtDNA molecules are coexisting. There are a set of recurrent point mutations in the mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) that are responsible for common mitochondrial diseases, including MELAS (mitochondrial encephalopathy, lactic acidosis, stroke-like episodes), MERRF (myoclonic epilepsy and ragged red fibers), LHON (Leber’s hereditary optic neuropathy), NARP (neuropathy, ataxia, retinitis pigmentosa), and Leigh syndrome. Mitochondrial disorders are clinically and genetically heterogeneous.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
